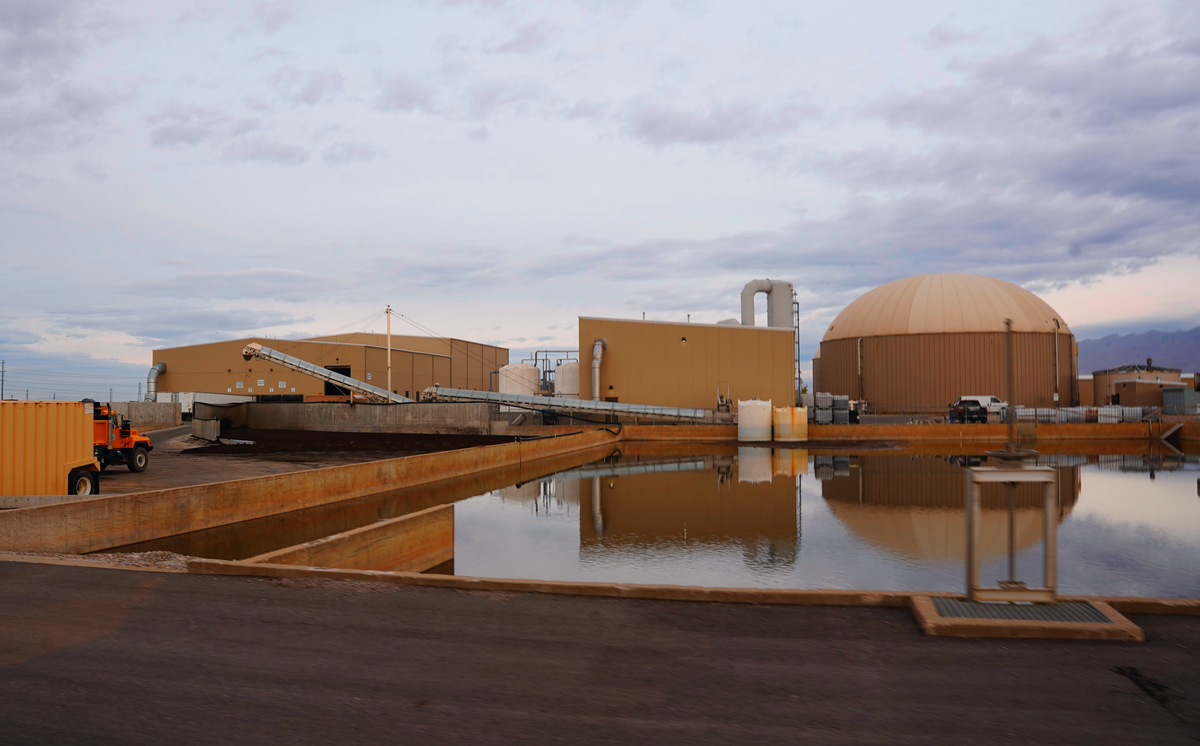


North Salt Lake, UT – November 14, 2025
OxEon Energy, a cleantech innovator at the forefront of sustainable fuel production, welcomed local industry leaders, government officials, and community partners to tour its newly operational Biogas-to-Oil (BTO) pilot plant on Friday, November 14. The event offered attendees an unprecedented look inside the R&D facility, where food waste and industrial biogas are converted into clean synthetic fuels, and highlighted the company’s broader strategy to scale solid oxide electrolysis (SOEC) manufacturing and develop Utah-based energy jobs.
From Vision to Pilot Plant
Jessica Elwell, OxEon’s Chief Operating Officer and co-founder, opened with remarks emphasizing the company’s dual mission: demonstrating advanced fuel technologies and building the next generation of U.S. manufacturing capacity. “Our DOE manufacturing scale-up project is how we are going to make this repeatable at commercial scale,” Elwell said. “This is where demonstration transitions into employment, building U.S. manufacturing capacity and Utah-based energy jobs as we go.”
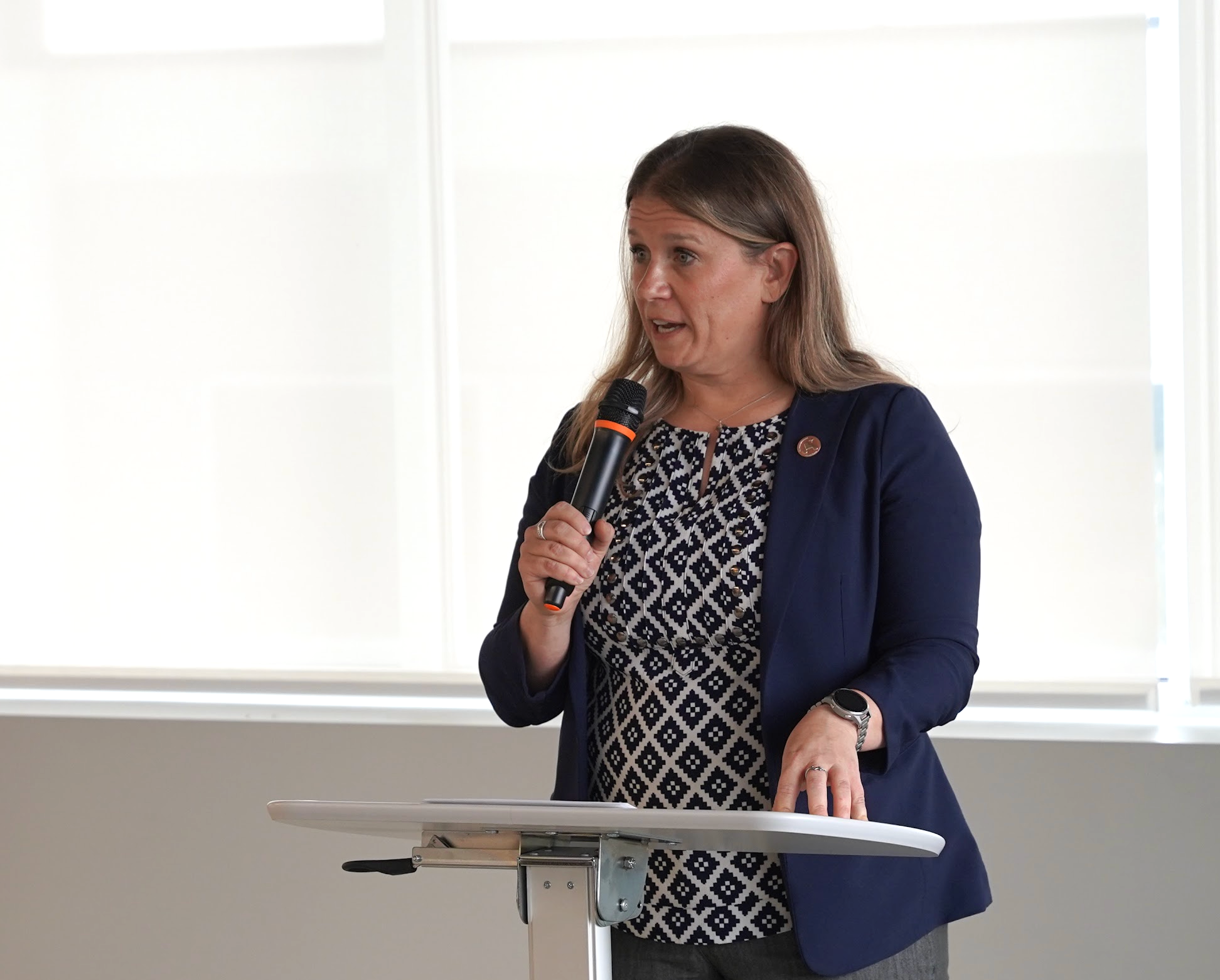

Elwell framed the event within a larger context of clean energy innovation in Utah, acknowledging the collaboration of state organizations, local industry partners, and community leaders who have supported OxEon’s work from its earliest days.
CEO and co-founder Joseph Hartvigsen shared both the company’s technical achievements and his own personal trajectory from aspiring rocket scientist to cleantech pioneer. Hartvigsen recounted his work on NASA’s MOXIE experiment aboard the Mars Perseverance Rover, which successfully produced oxygen from Martian CO₂. He emphasized how the technologies developed for space exploration are now being adapted for Earth-bound applications in sustainable fuel production.
Hartvigsen also highlighted the convergence of technology and market demand that has attracted multi-millions in investments to develop a world-class manufacturing and development facility in North Salt Lake, signaling the company’s rapid progress toward commercial-scale production.
Public-Private Partnerships in Renewable Gas
Matt Myers, General Manager at South Davis Sewer District, detailed the role of public-private partnerships in the project, particularly the Wasatch Resource Recovery facility. The facility processes local food waste from the Wasatch Front into renewable natural gas, which feeds directly into the local BP Enbridge pipeline. Myers explained the four streams of incoming waste—packaged foods, liquid waste like whey, fats/oils/greases, and residential or grocery store pickups—which all pass through hydrolysis and anaerobic digestion to produce methane. The remaining compost-like material is returned to local farms, creating a circular, sustainable process.
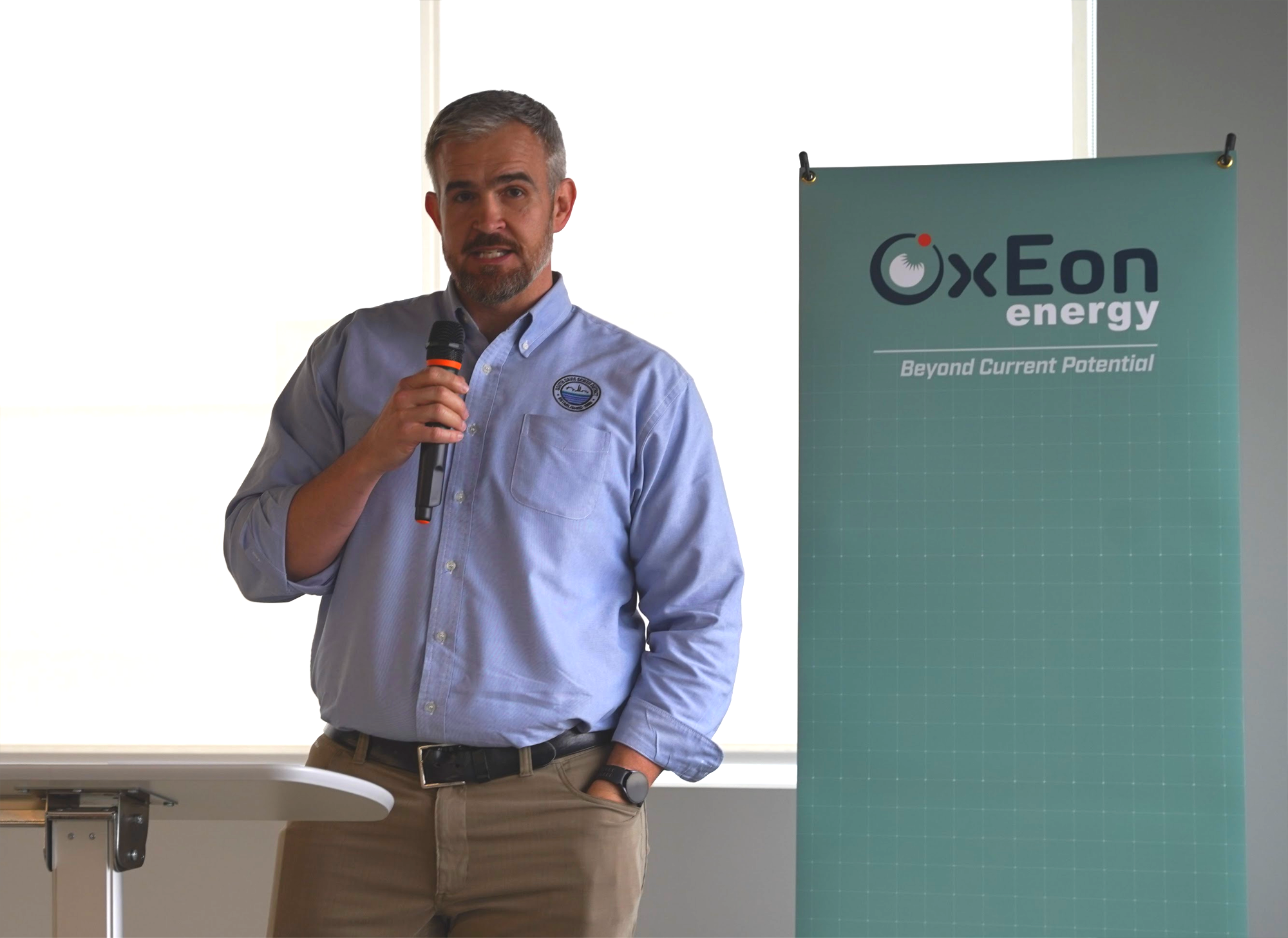

“This process takes about 21 days from the moment the waste hits our doors until methane is pulled off for use,” Myers said. He emphasized the importance of community engagement, noting that local households can participate in residential composting programs to support the facility’s input stream.
Synthetic Fuel Production: The Core of OxEon’s Innovation
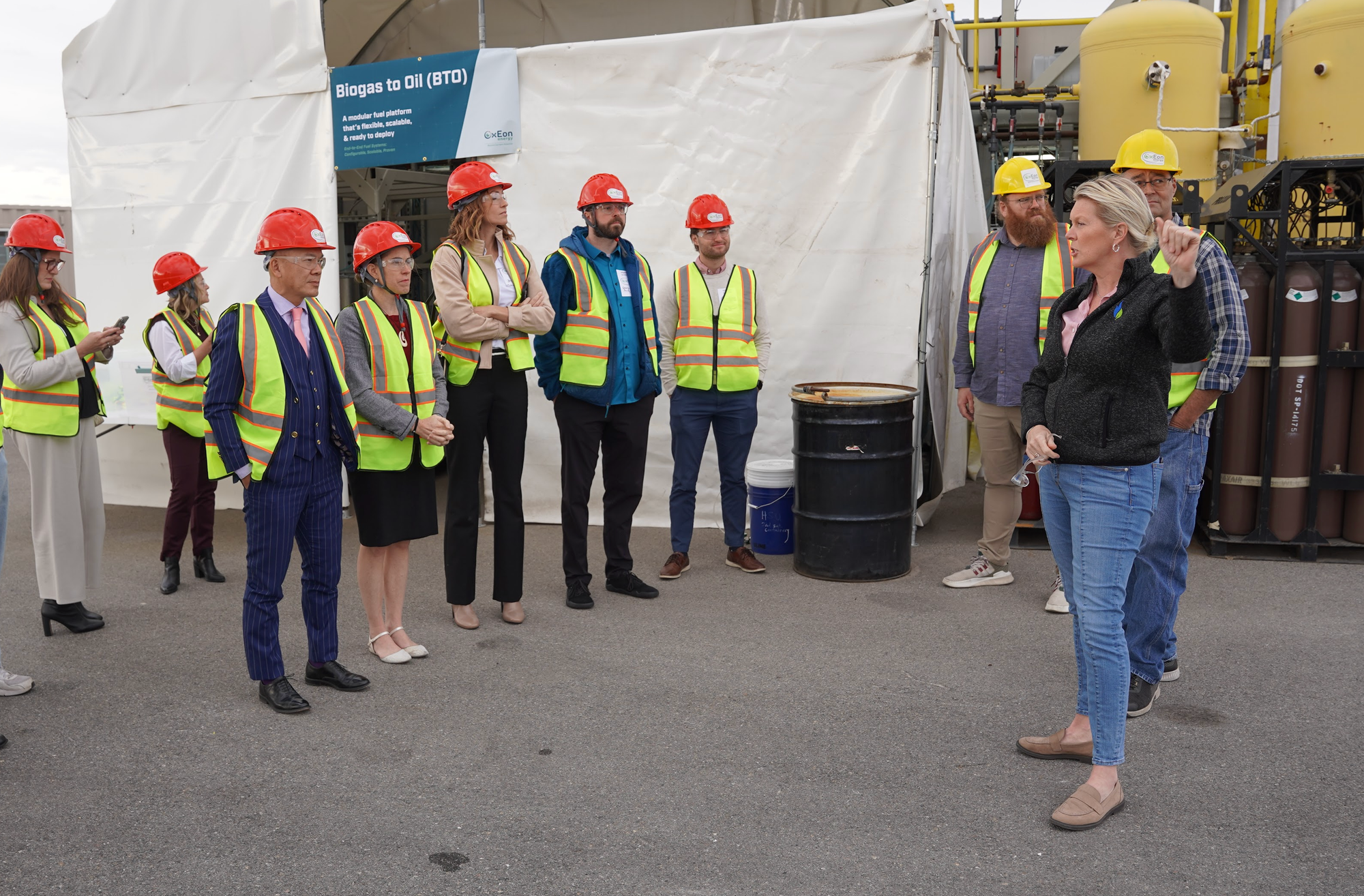

Michele Hollist, a chemical engineer at OxEon Energy, explained the various streams of food and industrial waste that feed OxEon’s renewable natural gas system. “We’re producing renewable natural gas right here on site, feeding it directly into the BP Enbridge pipeline,” she said. She pointed out the hydrolysis tank, digesters, and the main receiving area, describing how packaged foods, dairy byproducts, brewery waste, and fats, oils, and grease (FOG) are processed. Loose food waste from grocery stores and residential pickups is also handled with specialized equipment that separates packaging from organic material before it enters the digesters.
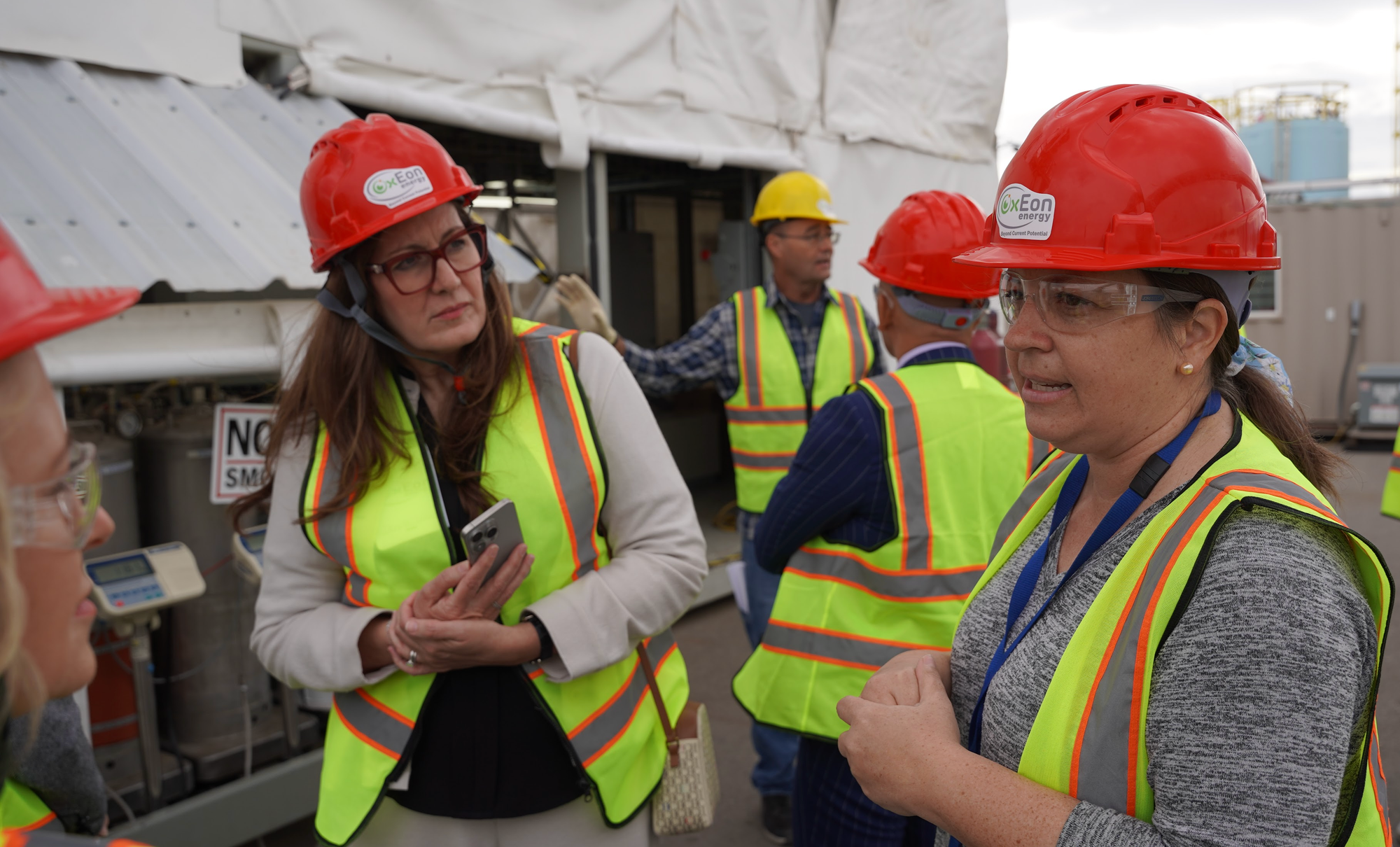

She emphasized community participation in the process, noting Momentum Recycling, a local residential food waste collection service. Neighborhoods participating in Momentum’s program have their food waste picked up and delivered to Wasatch Resource Recovery, where it is converted into renewable natural gas and nutrient-rich fertilizer, reinforcing the circular carbon economy in the region. She explained that from the moment waste arrives at the facility, the digestion process takes roughly 21 days, after which the remaining material is dried and used on local farms, completing the loop from waste to energy and back to the soil.
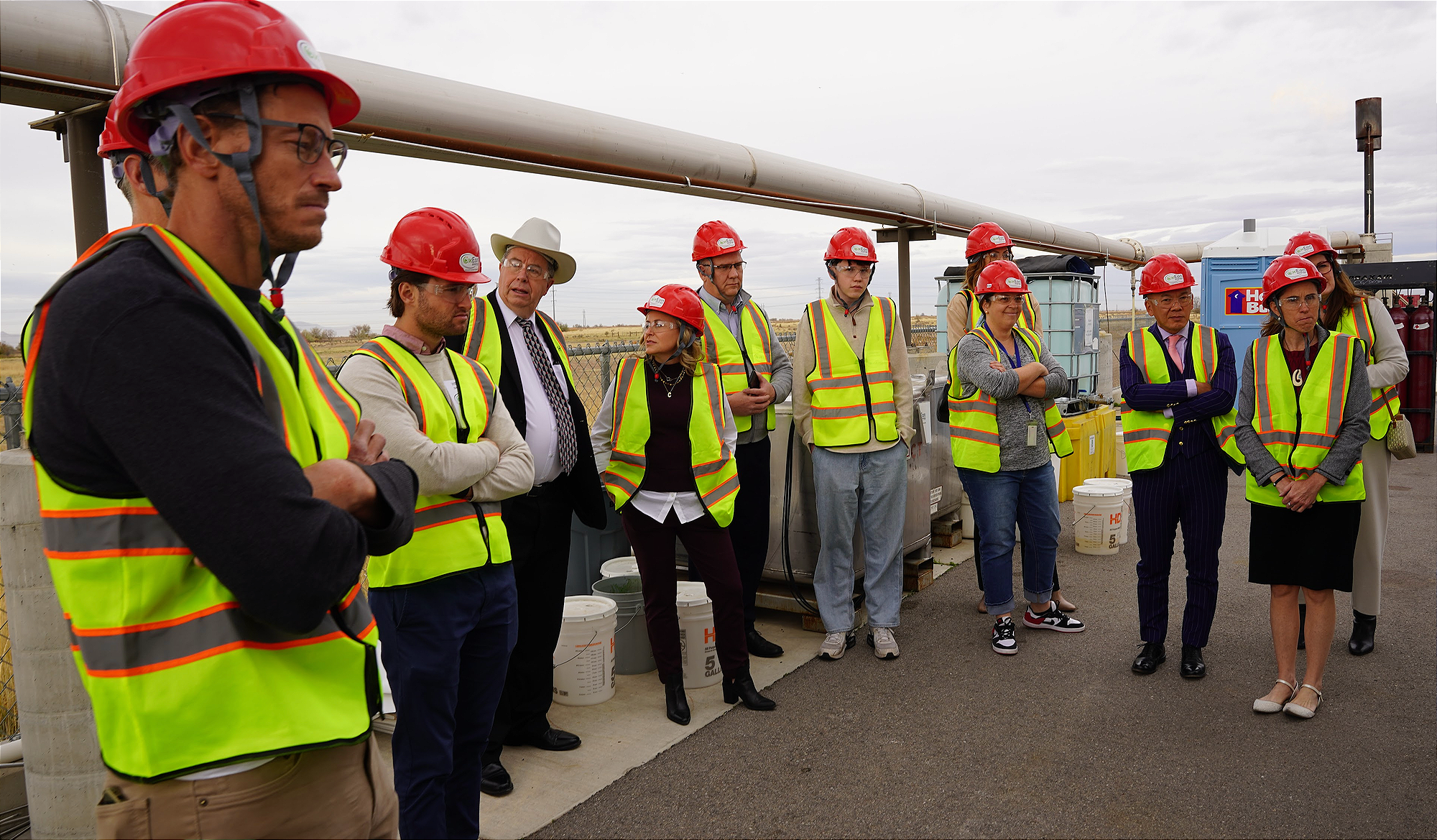

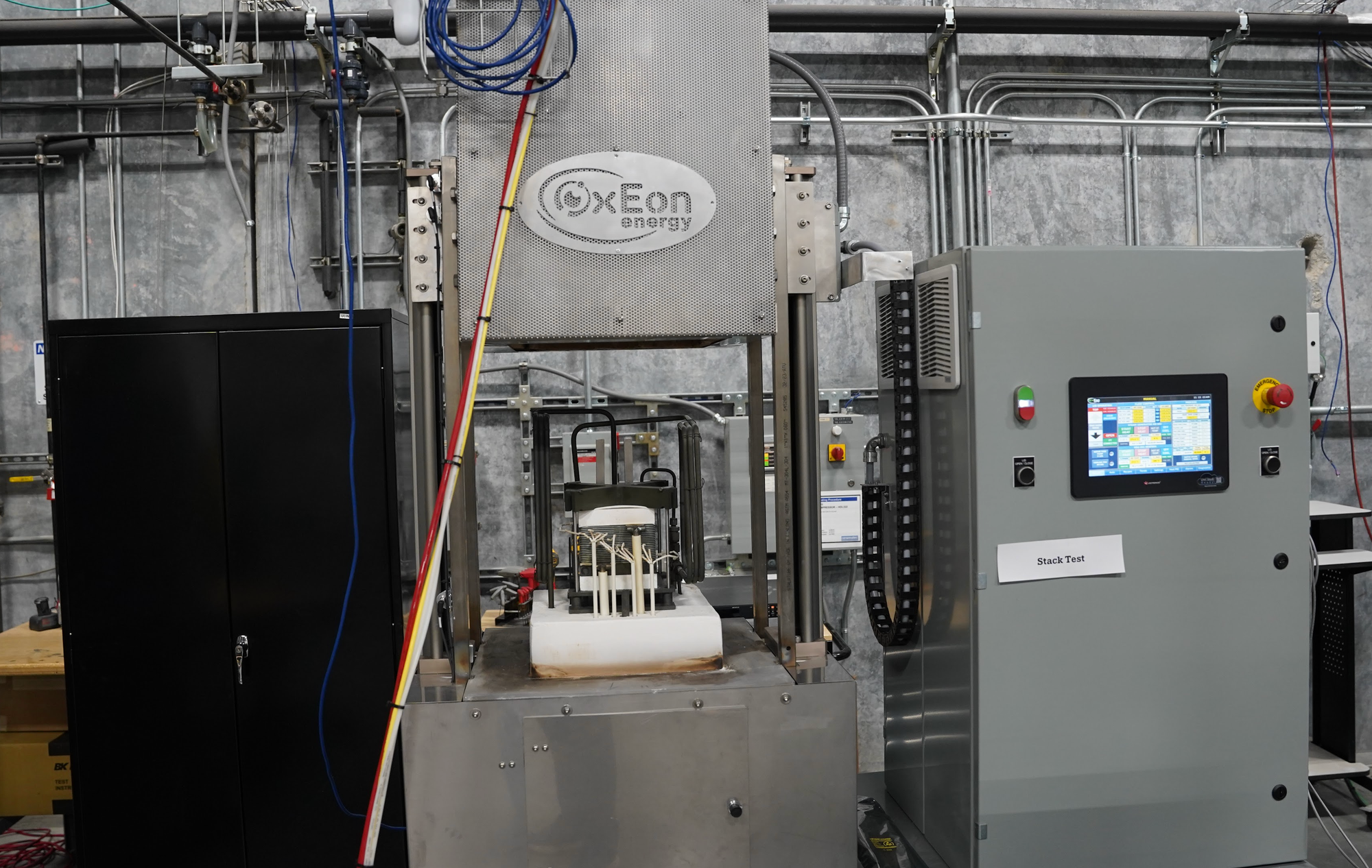
Additional demonstration locations across the large facility highlighted the integration of solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs). These reversible devices can electrolyze CO₂ and water to produce oxygen, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen, which can then feed the Fischer–Tropsch process or be used in fuel cells to generate electricity. The facility includes research and pilot-scale stacks, with cells being tape-cast, dried, sintered at extreme temperatures, and coated with specially engineered electrodes to improve performance and stability.
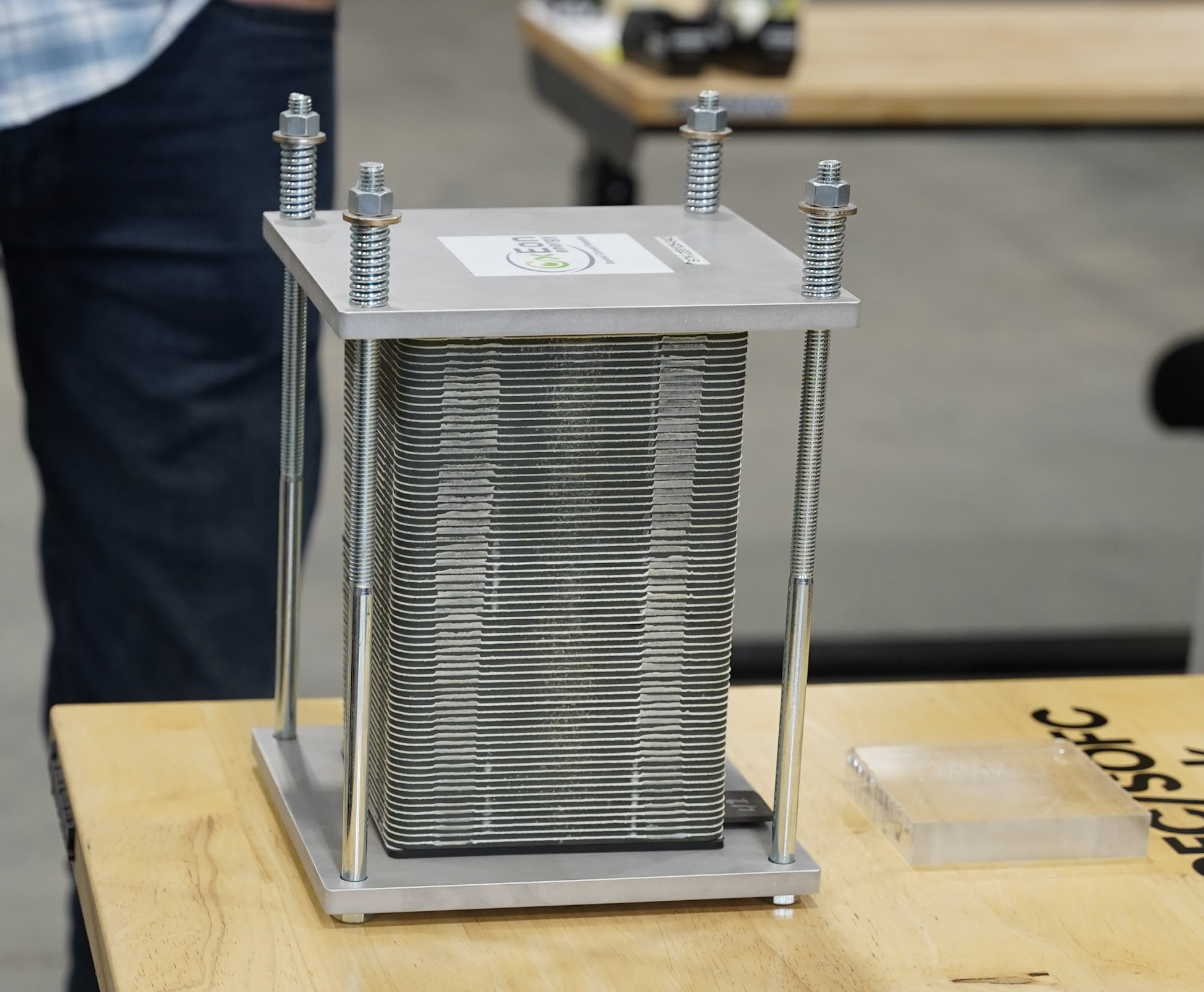
Visitors observed both small “button cells” used in R&D and full-scale stacks suitable for industrial applications.
Scaling Manufacturing: DOE Support and Automation
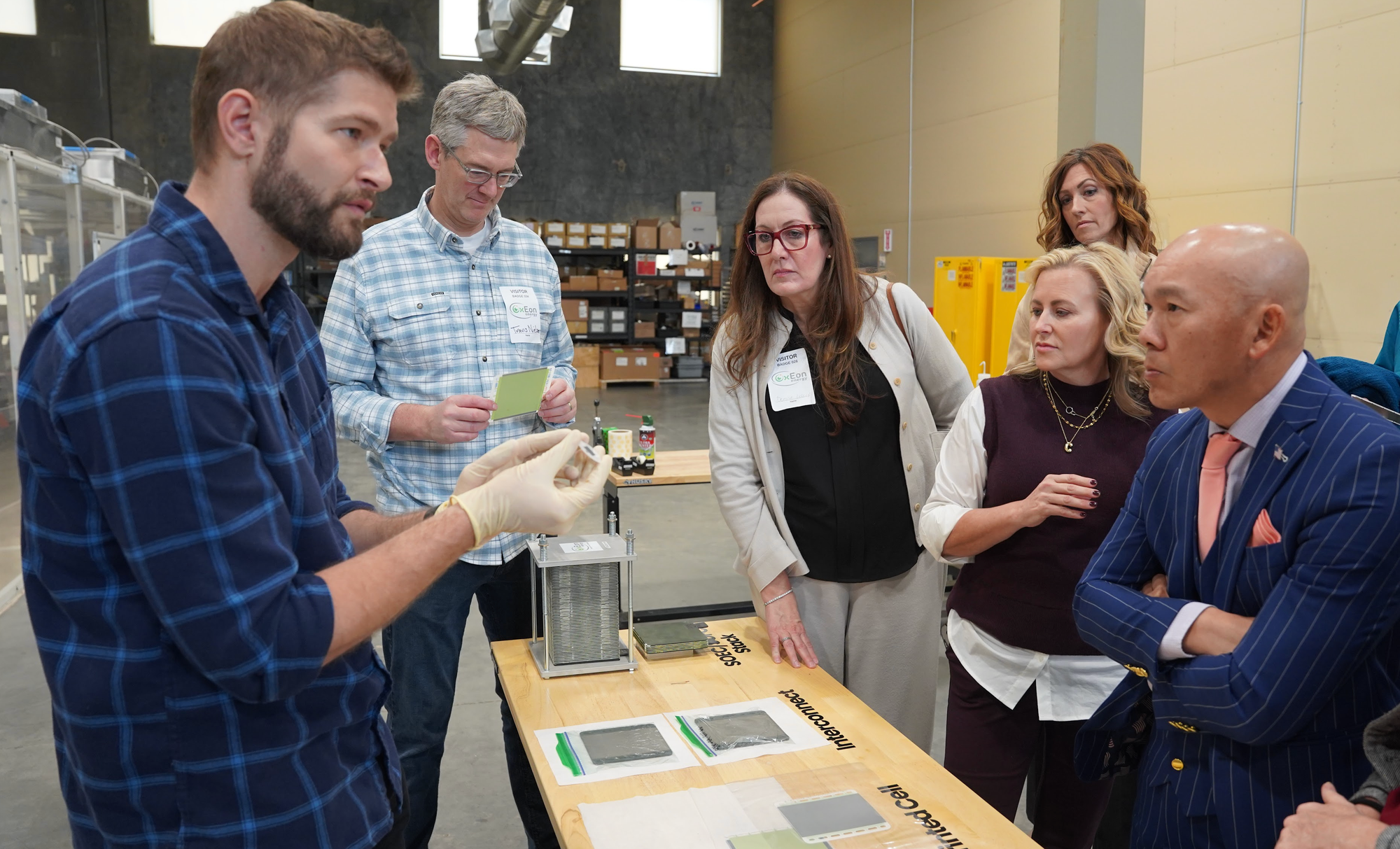
The tour also offered insight into OxEon’s DOE-supported manufacturing scale-up, building on a $36 million grant under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law awarded in 2024. The funding is intended to propel SOEC manufacturing to a 25 MWe annual production capacity, streamline processes, reduce stack costs, and serve as a steppingstone toward a full Gigawatt-scale facility.
Key aspects of the scale-up include:
- Automation Evolution: Transitioning from hand-applied electrodes and manual stack assembly to automated production lines to increase throughput and reduce labor costs.
- Quality Control: Implementing in-line inspection and testing to ensure uniformity, durability, and performance.
- Strategic Collaborations: Partnering with JR Automation, ASYS Group, ONEJOON Inc., Silverstone Automation, and universities such as the University of Utah and Georgia Institute of Technology to optimize manufacturing and develop workforce pipelines.

Advanced Research and Defense Applications
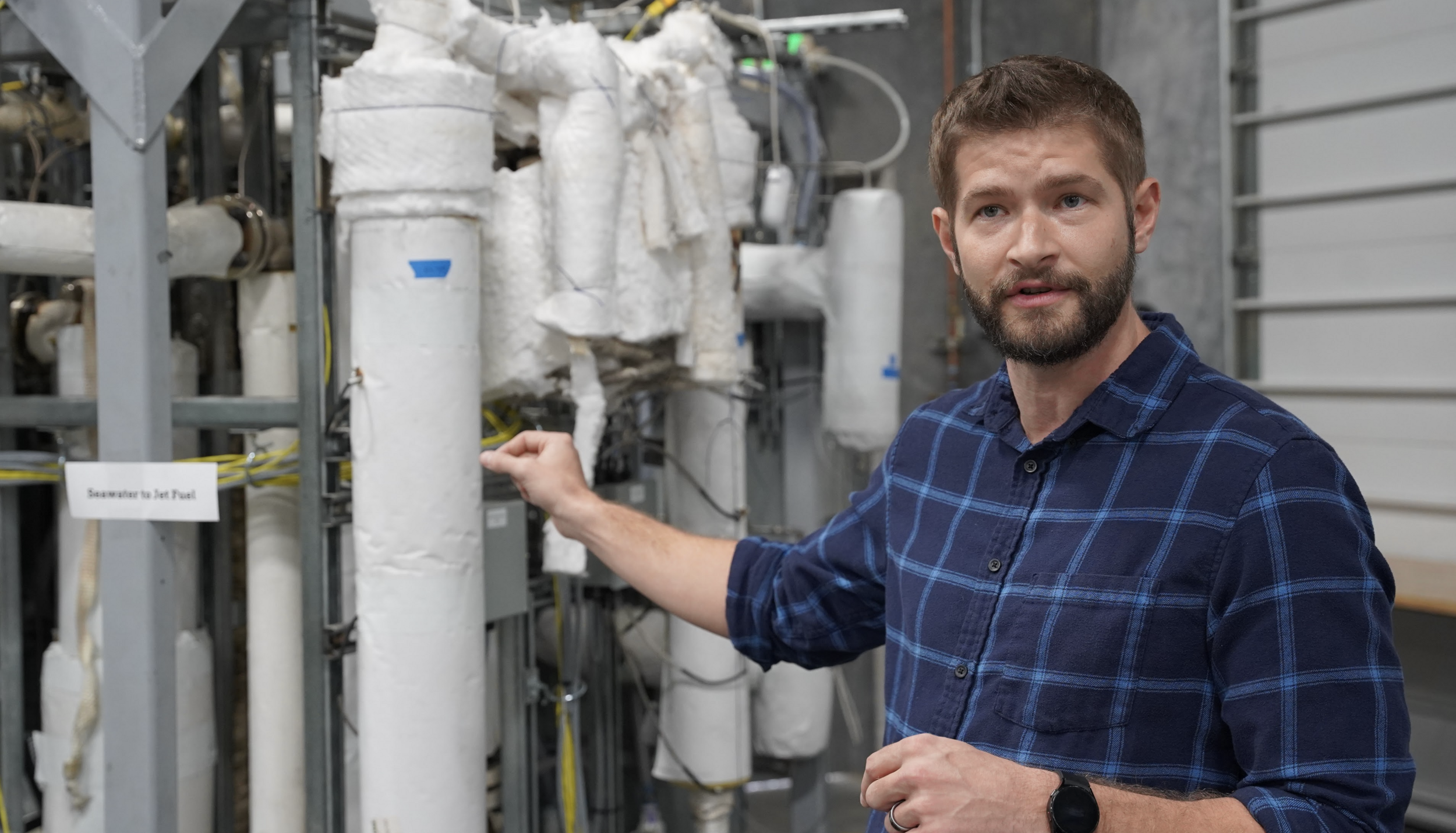
Beyond Earth-bound energy production, OxEon continues to leverage its technologies for defense and aerospace applications. The company is developing modular systems for the U.S. Navy to convert CO₂ from seawater into jet fuel, potentially enabling fuel production anywhere in the world and reducing vulnerability of military supply chains. These systems demonstrate how the same Fischer–Tropsch and SOEC technologies that drive renewable aviation fuels can be adapted for remote or constrained environments.

Aaron Starks, CEO of 47G, Utah’s Aerospace and Defense Association, underscored the significance of these capabilities for national security. “The space economy is going to be worth over a trillion dollars in the next ten years,” Starks said. “OxEon’s work demonstrates that Utah is producing founders and entrepreneurs who are building next-generation technology with real-world impact.”

From MOXIE to Earth-Bound Fuels
Visitors were reminded of the origins of OxEon’s SOEC technology, first proven aboard NASA’s Mars Perseverance Rover via the MOXIE experiment. The success of MOXIE, which generated oxygen from Martian CO₂, laid the foundation for scaling these devices to produce syngas and synthetic fuels on Earth. By leveraging the same core electrochemical processes, OxEon has transitioned from space exploration to industrial-scale fuel production, showing how high-tech innovation can be translated from extreme environments to practical energy solutions.
The facility’s engineers also demonstrated upcoming improvements, including automated electrode printing, expanded cell sizes, and integration of SOEC stacks into modular fuel synthesis systems. These enhancements are expected to increase efficiency, lower costs, and accelerate deployment of renewable fuels for aviation, trucking, and marine transport.

Circular Carbon Economy in Action
A central theme throughout the tour was the circular carbon economy: capturing carbon from waste and converting it into high-value fuels while creating renewable natural gas and compost for local agriculture.
Tour visitors saw firsthand the transformation of food waste from local grocery stores, restaurants, and households into methane, syngas, and finally into liquid fuels. The remaining organic material, heated and dried, becomes a nutrient-rich soil amendment for local farms, demonstrating a complete cradle-to-cradle approach.
Workforce Development and Community Impact
OxEon emphasized that the company’s growth is closely tied to community engagement and workforce development. In addition to internships and apprenticeships, the company partners with universities and research labs, fostering local talent in energy technology, advanced manufacturing, and electrochemical research. The DOE-backed scale-up will further expand these opportunities, creating high-paying, sustainable jobs in Utah’s energy and cleantech sectors.

Looking Ahead
As OxEon Energy moves from demonstration to commercial deployment, the North Salt Lake pilot facility serves as both a testing ground and showcase for the company’s vision: sustainable, circular, and economically viable fuel production.
Elwell closed the event noting, “This facility is proof that Utah can lead in advanced manufacturing and clean energy innovation. What starts here in our pilot plant will soon scale to meet industrial needs globally, proving that sustainable fuels can be both technically achievable and economically viable.”
With the BTO pilot plant in North Salt Lake now fully operational, OxEon Energy continues to bridge the gap between space-age electrochemistry and practical energy solutions, turning local waste streams into high-value fuels and showcasing Utah as a hub for cleantech innovation.

Learn more at oxeonenergy.com.

